Agri-Tech Adaptation: Benefits for Stakeholders
- Editor
- February 14, 2025
- News, Technology
- Technology
- 0 Comments

Dr. Selvanathan Anojan

Dr. Selvanathan Anojan is a leading expert in agriculture and technology, recognized for his efforts in democratising agricultural innovations and creating practical, low-cost agrisolutions for farming communities. As the co-founder and Secretary of the Sri Lanka Agripreneurs’ Forum (SLAF), Assistant Secretary General at The Ceylon Chamber of Commerce (CCC), and a member of the Presidential Taskforce on Agriculture, he has significantly contributed to advancing Sri Lanka’s agricultural sector.
What is Agritech, and why is it important for modern agriculture?
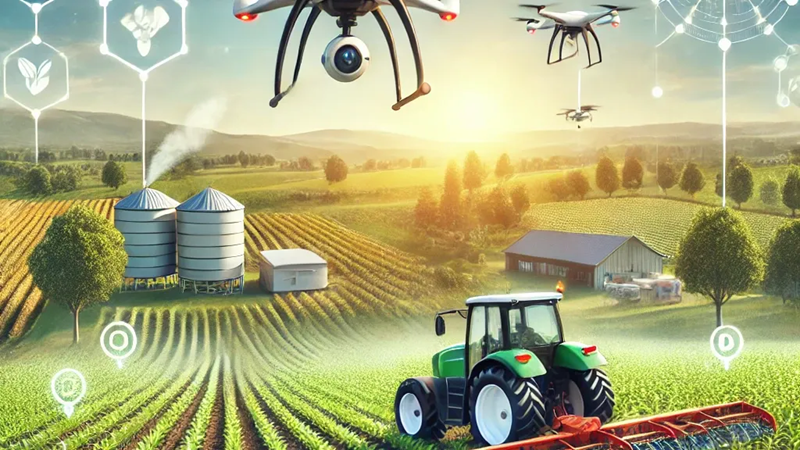
Agritech, short for agricultural technology, refers to the use of innovative technologies like Precision Agriculture Tools, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain Technology, Drones, Satellite Imagery, Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors, Geospatial Technology, Smart Irrigation Systems, Farm Management Software, Predictive Analytics Tools, Agri-Fintech Solutions, Digital Marketplaces, Crowdfunding Platforms, Mobile Payment Solutions, Remote Sensing Technologies, Weather Forecasting Systems, Agricultural Robotics, Agrochemical Application Technologies, Soil Health Monitoring Tools, Supply Chain Traceability Tools, Biotechnology Solutions, e-Extension Services, Digital Lending Platforms, Automated Greenhouses, Seed and Input Marketplaces, Genetically Modified Crops, Vertical Farming Technologies, Smart Contract Platforms, Cloud-based Data Platforms, Farmer Networking Apps, Livestock Monitoring Systems to improve the agriculture sector.
As global food demand rises and climate change disrupts traditional farming methods, agritech offers efficient, sustainable solutions. It helps farmers increase yields, reduce waste, conserve water, and improve overall productivity, making agriculture more resilient and profitable in the long run.
How does agritech impact smallholder farmers?
Smallholder farmers, who make up a large percentage of agricultural producers globally, often face challenges such as limited resources, unpredictable weather patterns, and poor access to markets. Agritech can significantly improve their livelihoods by providing real-time data on weather, soil conditions, and crop health, enabling them to make more informed decisions. For instance, low-cost sensors and satellite data can monitor soil moisture and nutriant levels, while mobile apps provide access to agricultural best practices, helping farmers optimize their resources and reduce costs.
What role do drones and satellite data play in agritech?
Drones are transforming precision agriculture by not only monitoring large areas of farmland but also applying fertilizers and agrochemicals with pinpoint accuracy. This precision ensures that only the necessary amount of chemicals is used, reducing waste and environmental impact while optimizing crop health.
In addition to drones, various types of satellites play a crucial role in monitoring multiple aspects of farm health. Satellites can assess soil quality, track groundwater levels, detect pest infestations, and monitor crop diseases. These insights help farmers take proactive measures, ensuring timely interventions and minimizing losses. The combination of drones and satellite data offers a powerful, data-driven approach to enhancing farming efficiency and sustainability.
How can agritech reduce the environmental impact of farming?
Agritech helps make farming more environmentally friendly by promoting efficient resource use and reducing chemical inputs. For instance, AI-powered irrigation systems ensure that crops receive only the necessary amount of water, conserving water in drought-prone areas. Automated machinery minimizes soil compaction, and precision spraying techniques ensure pesticides are applied only where needed. These innovations lead to less environmental degradation, improved soil health, and lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to sustainable farming practices.
What are the financial benefits for farmers adopting agritech solutions?
Farmers who adopt agritech can experience increased profitability through cost savings and higher yields. Precision farming technologies allow them to reduce input costs, such as seeds, water, and fertilizers, while maximizing crop output. Additionally, better crop management means fewer losses due to pests or diseases, leading to higher quality produce and better prices in the market. Over time, these financial gains outweigh the initial investment in technology, making it a smart long-term decision for farmers.
How does agritech benefit governments and policymakers?
For governments and policymakers, agritech presents an opportunity to enhance food security and boost agricultural productivity. Data collected from smart farming systems can inform policy decisions, helping governments allocate resources more effectively. It also helps in identifying regions that need support due to changing climate conditions or crop failures. By supporting agritech, governments can ensure sustainable agricultural practices, reduce dependency on imports, and increase the competitiveness of local farmers in global markets.
What role do agribusinesses and investors play in agritech adaptation?
Agribusinesses and investors are key stakeholders in promoting agritech. By investing in technology startups and innovative farming solutions, they drive the development and deployment of new tools that benefit the entire agriculture ecosystem. Agribusinesses benefit from more efficient supply chains, improved crop quality, and stronger relationships with farmers who adopt their technologies. For investors, agritech offers attractive returns due to the growing demand for food production and sustainable farming practices.
How does agritech improve food safety and traceability?
Agritech enhances food safety and traceability by digitizing the supply chain. Sensors and blockchain technology can track products from farm to table, ensuring that produce meets quality standards and is free from contaminants. This transparency boosts consumer confidence and allows regulatory bodies to enforce food safety regulations more effectively. In case of contamination or foodborne illnesses, it also helps in pinpointing the source quickly, reducing the impact of product recalls and protecting public health.
What are the challenges of implementing agritech in developing countries?
While agritech offers significant benefits, its adoption in developing countries faces several challenges, including high initial costs, limited infrastructure, and lack of technical knowledge among farmers. Access to reliable internet and electricity is essential for many agritech solutions, but these are often lacking in rural areas. Additionally, smallholder farmers may be hesitant to invest in technology without guaranteed returns. Governments, NGOs, and the private sector must collaborate to provide subsidies, training programs, and infrastructure development to overcome these barriers.
What is the future outlook for agritech and its stakeholders?
The future of agritech is promising, with advancements in AI, robotics, and biotechnology set to further transform agriculture. As these technologies become more affordable and accessible, we can expect to see widespread adoption among farmers, especially in regions struggling with climate change and resource constraints. Stakeholders, including farmers, agribusinesses, governments, and consumers, will benefit from increased food security, improved environmental sustainability, and higher economic returns. Agritech will play a critical role in shaping a resilient and sustainable global food system for future generations.
In conclusion, agritech is not just a technological innovation but a necessary evolution in agriculture. By embracing these tools, stakeholders at every level; from smallholder farmers to large agribusinesses and governments, can address the growing challenges in food production, sustainability, and profitability. The adoption of agritech solutions has the potential to revolutionize the agricultural landscape, ensuring food security and improved livelihoods for millions of people worldwide.